Covid reinfection risks include Long Covid and organ damage.
How long after the previous infection is it considered a reinfection
A Nature study defines reinfection as a Covid case occurring at least 60 days after the first infection. Ongoing symptoms within this timeframe are attributed to the same infection.
In practice, the CDC recommends testing from 30 days after your last infection. Particularly, this includes people who suspect they have Covid even if they have no symptoms.
Vaccines reduce some of the risk of Covid reinfection
From a 2023 study, original vaccines are 60.4% effective against Omicron at one month and 13.3% effective at nine months after vaccination.
A 2024 Nature study found vaccination provides longer protection against reinfection than natural protection. Evidently, unvaccinated people got reinfected at a median of six months after an infection compared to 14 months for vaccinated people.
However, a three-dose vaccination regime was better than a two-dose regime in previously uninfected individuals based on a 2023 study.
Symptoms of a Covid infection
The CDC estimates the March 2025 US Covid strains as LP8.1 at 47% and XEC at 26%. These have similar symptoms to prior strains.
Per the CDC, possible Covid symptoms include:
- Fever or chills
- Cough
- Shortness of breath or difficulty breathing
- Sore throat
- Congestion or runny nose
- New loss of taste or smell
- Fatigue
- Muscle or body aches
- Headache
- Nausea or vomiting
- Diarrhea
A key danger of Covid reinfection is Long Covid
A 2024 preprint showed that people with two infections were more than twice as likely to report Long Covid than those with one infection. Accordingly, people with three Covid infections have an almost quadrupled risk.
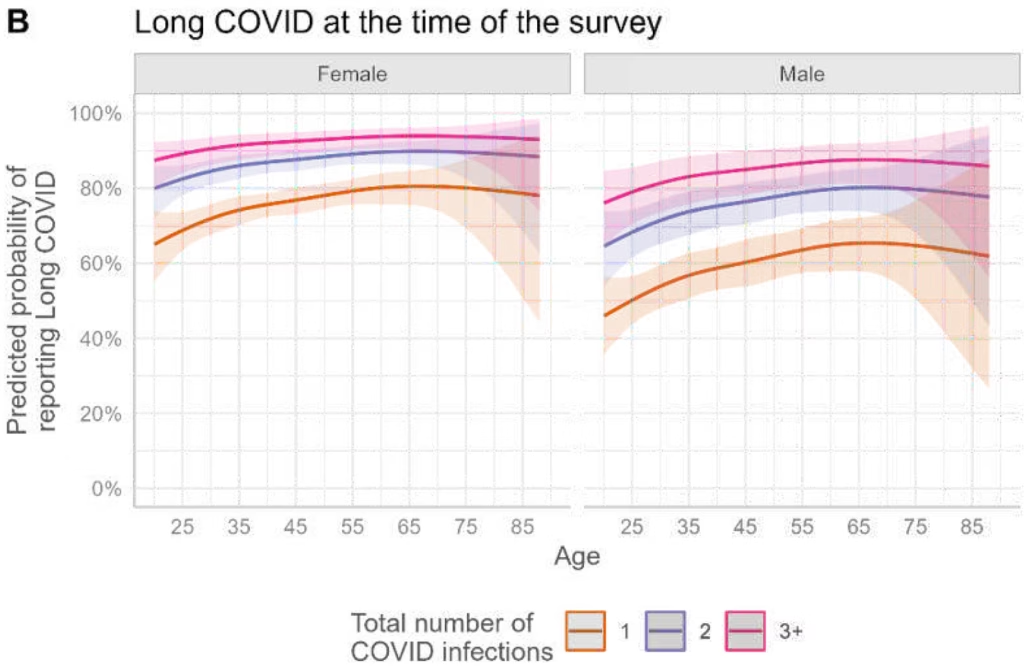
The CDC defines Long Covid as ” a chronic condition that occurs after SARS-CoV-2 infection and is present for at least 3 months.”
It is a debilitating condition. For example, I have Long Covid and I am confined to my bed for over 95% of my day. I am unable to work. The prognosis is poor.
Covid reinfection causes further IQ loss
In one study, a mild and resolved Covid infection resulted in a three-point loss of IQ. Those with persistent symptoms such as fatigue showed a six-point loss of IQ. A reinfection contributed an additional 2-point IQ loss. The average person has an IQ of 100.
Covid reinfection may cause organ damage
A 2022 Nature study showed that reinfection raised the risk of death, hospitalization and disorders affecting the lungs, heart, brain, blood, musculoskeletal and gastrointestinal systems. It also contributes to diabetes, kidney disease and mental health issues.
Vulnerable groups are at higher risk
The studies above apply to a cross section of the population. Vulnerable groups are particularly at risk from an additional Covid infection. The CDC considers vulnerable groups to include over 50s, some racial and ethnic minority groups, people with underlying medical conditions.

